Circulating CC16 and Asthma: a Population-Based, Multi-Cohort Study from Early Childhood Through Adult Life
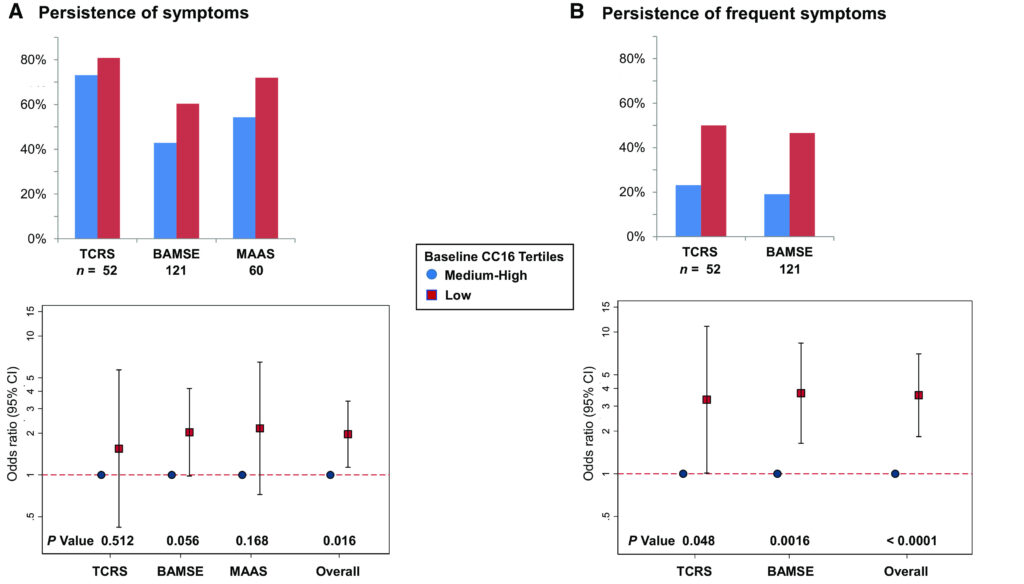
Rationale: Club cell secretory protein (CC16) is an antiinflammatory protein highly expressed in the airways. CC16 deficiency has been associated with lung function deficits, but its role in asthma has not been established conclusively. Objectives: To determine 1) the longitudinal association of circulating CC16 with the presence of active asthma from early childhood through adult life and 2) whether […]
Trajectories and Early Determinants of Circulating CC16 from Birth to Age 32 Years
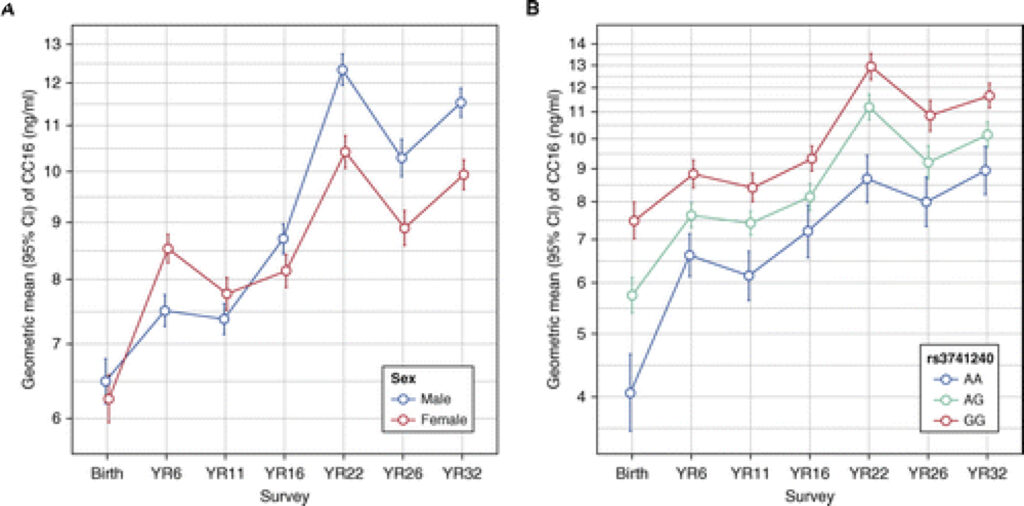
The club cell secretory protein CC16 is a pneumoprotein present in circulation but mainly produced by club cells and other nonciliated airway epithelial cells (1–3). Its biological functions have not been conclusively elucidated, but findings from in vitro studies (4) and mouse models (5) support antiinflammatory and antitoxicant properties of CC16 in the lung. In line with […]
Effects of Retinoids on Augmentation of Club Cell Secretory Protein
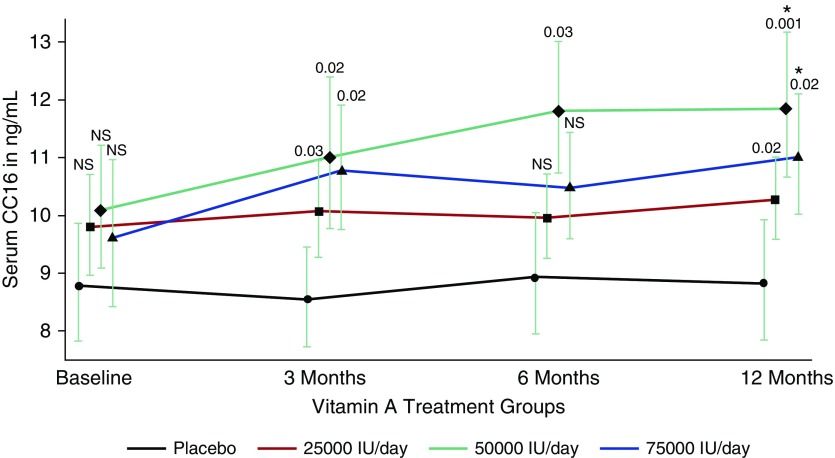
Club cell secretory protein (CC16; encoding gene, SCGB1A1) is a homodimeric pneumoprotein that is produced mainly by club cells and other nonciliated epithelial cells in both proximal and distal airways (1). Higher airway expression and circulating levels of CC16 have been associated cross-sectionally with better lung function and lower prevalence and severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary […]
Club Cell Secretory Protein in Serum and Bronchoalveolar Lavage of Patients with Asthma

Club cell secretory protein (CC16) is a homodimeric pneumoprotein that is mainly produced by nonciliated bronchial epithelial cells1,2 and is found both in the airways and in the circulation. The biological functions of CC16 have not been conclusively determined, but in vitro, ex vivo, and animal studies indicate anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antitoxicant properties of this molecule in the lungs.1,2 Clinical […]
The Relation of Circulating CC16 to Lung Function Growth, Decline, and Development of COPD Across the Lifespan
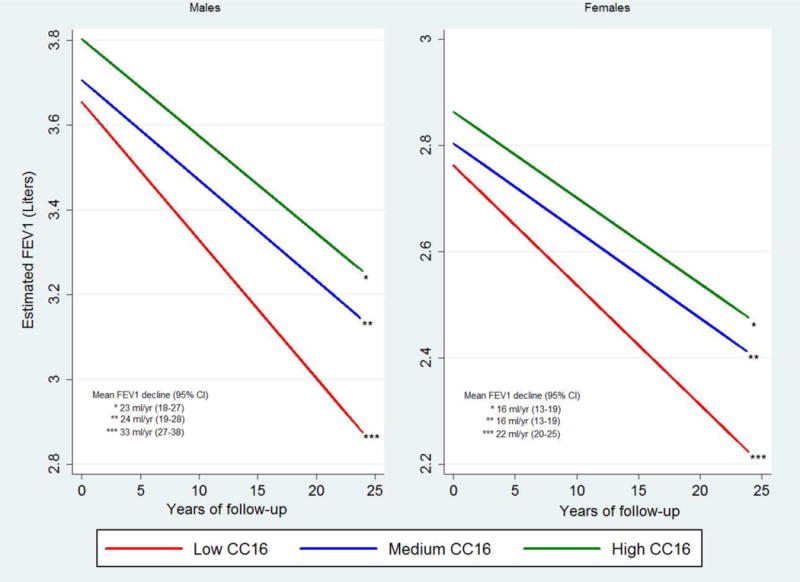
Background Low serum levels of the anti-inflammatory club cell secretory protein (CC16) have been associated with an accelerated FEV1 decline in COPD. Whether low circulating CC16 precedes lung function deficits and incidence of COPD in the general population is unknown. Methods We used longitudinal data from adults who were COPD-free at baseline from the population-based […]
